
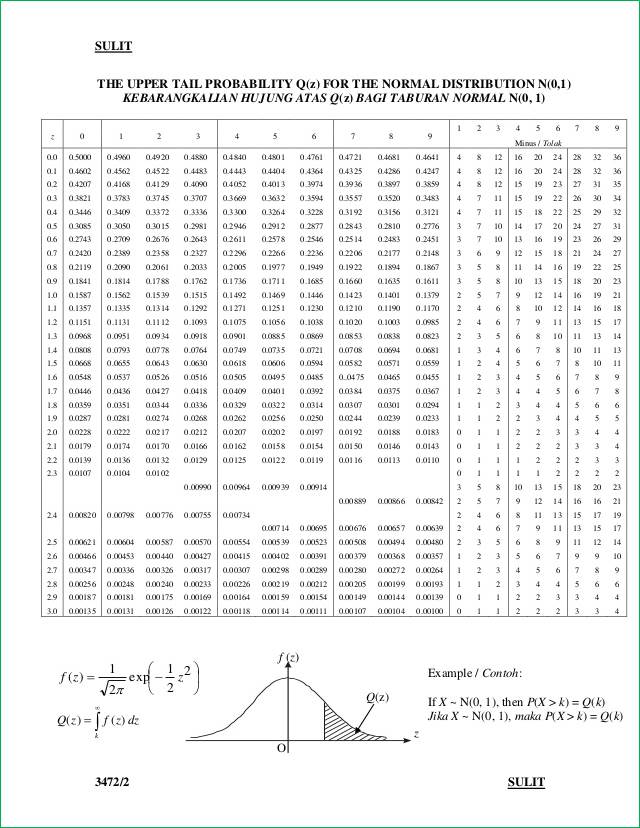
See Figure 5.23 "Computation of the Number ". To begin with, we must first subtract 0.01 from 1 to find the area 1 − 0.0100 = 0.9900 of the left tail cut off by the unknown number z. 01 first, and it is instructive to rework the problem this way. We could just as well have solved this problem by looking for z.
/dotdash_Final_The_Normal_Distribution_Table_Explained_Jan_2020-01-091f853d86c444f3bd7cd32c68fc0329.jpg)
01 = − 2.33, we conclude immediately that z. The answer to the second half of the problem is automatic: since − z. 01 we use the heading of the column that contains 0.0099, namely, 0.03, and write − z. The number 0.0099 is closer to 0.0100 than 0.0102 is, so for the hundredths place in − z.
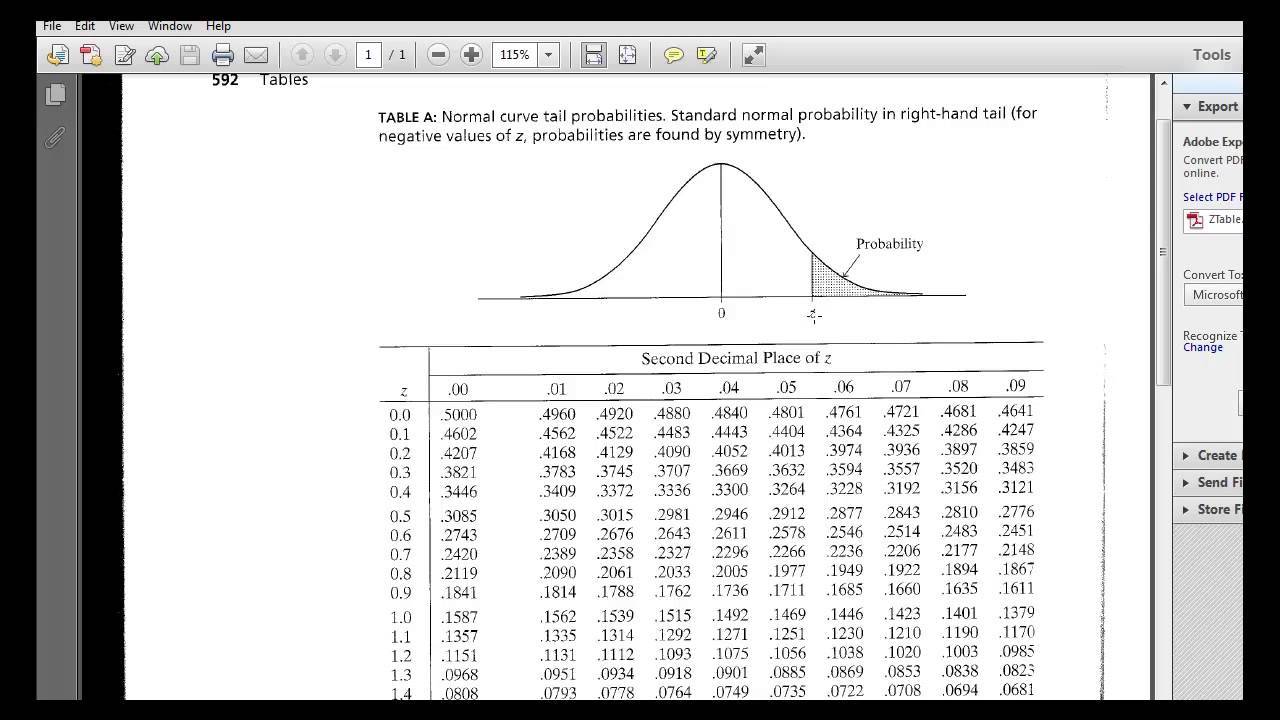
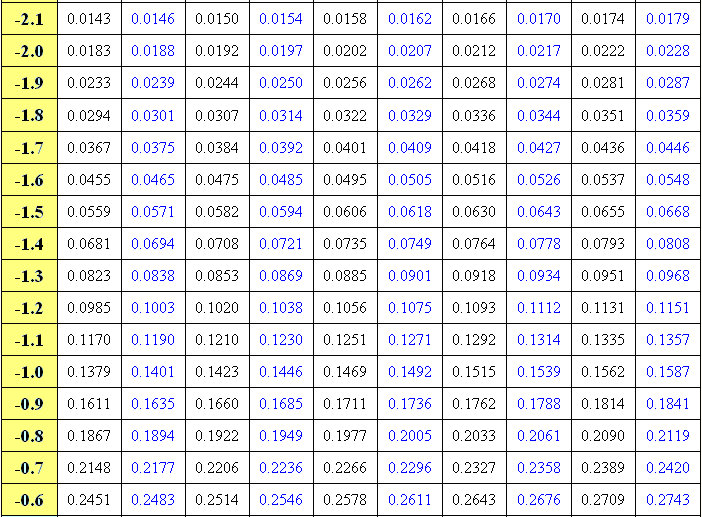
It is not there, but falls between the two numbers 0.0102 and 0.0099 in the row with heading −2.3. 01 cuts off a left tail of area 0.01 and Figure 12.2 "Cumulative Normal Probability" is a table of left tails, we look for the number 0.0100 in the interior of the table. 01, the values of Z that cut off right and left tails of area 0.01 in the standard normal distribution. Normal probability distribution function at 1.Find z. Normal cumulative distribution function at 1.333333 If you need to, you can adjust the column widths to see all the data. For formulas to show results, select them, press F2, and then press Enter. The equation for the standard normal density function is:Ĭopy the example data in the following table, and paste it in cell A1 of a new Excel worksheet. If z is nonnumeric, NORM.S.DIST returns the #VALUE! error value. If cumulative is TRUE, NORMS.DIST returns the cumulative distribution function if FALSE, it returns the probability mass function.
Cumulative is a logical value that determines the form of the function. The value for which you want the distribution.Ĭumulative Required. The NORM.S.DIST function syntax has the following arguments: Use this function in place of a table of standard normal curve areas. Returns the standard normal distribution (has a mean of zero and a standard deviation of one).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
